Sugar overloading the body leads to strokes, limb amputations, infections, and many other devastating consequences in the 30 million people throughout the United States who are affected by diabetes. Type 2 diabetes is by far the most common, contributing to 95% of all cases of diabetes mellitus (1).
While it's clearly a very serious disease, type 2 diabetes can often be both prevented and cured.
Even though diabetes is the 7th leading cause of death in the US, it's also the leading preventable illness in the country (2).
This article focuses on type 2 diabetes, it's dangers and how changing your diet can be a cure.
What is Diabetes Mellitus?
Diabetes mellitus is a disease rooted in high blood sugar because of problems with a hormone called insulin. Because carbohydrates are broken down into sugars after you eat them, they are also referred to as “sugars” in these discussions.
Blood glucose is the technical term for sugars in our body.
Glucose is critically important for life - providing your brain, muscles and other organs in your body precious fuel it needs to survive.
But there can be too much of a good thing. Uncontrolled levels of glucose can be deadly.
Insulin & Blood Glucose
Insulin is an important hormone in charge of helping the cells in your body to use glucose. Insulin can be thought of as a key that ‘opens the door’ and allows glucose to enter every cell in our body. Glucose then gives cells the energy they need to function.
Insulin also helps to put extra glucose into storage. Stored glucose is called glycogen. Insulin helps to store this extra glucose in your fat, muscles and liver. If you skip a meal, or need extra energy for any other reason, your body can break down this glycogen into free glucose.
Glucose levels are highest in the bloodstream after you eat, as your food is digesting. Higher levels of glucose stimulates more insulin to be released by beta cells in your pancreas. It makes sense that insulin should also be the highest after you eat to help use and control the high blood glucose circulating in your body.
Normal blood glucose typically ranges from 80-130. When insulin is doing its job, it keeps these levels regulated by both allowing cells to access the energy they need and also storing excess glucose.
Insulin works so well in healthy individuals that it usually prevents glucose from ever going above 180, even after eating sugary treats (3).
If insulin isn’t working properly then blood glucose levels can rise dramatically and dangerously - which is what happens in diabetics.
Type 1 Diabetes
There are two forms of diabetes: type 1 and type 2. People with type 1 diabetes represent only about 5-10% of the population with diabetes mellitus (4) . Their bodies aren’t able to produce insulin. While it’s very important that people with type 1 diabetes carefully monitor their diet, an unhealthy diet wasn't the cause of their diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes is caused by an autoimmune condition that damages the cells that make insulin (beta cells in the pancreas).
We unfortunately aren’t able to predict or prevent who will develop type 1 diabetes. Because they don’t make insulin, people with type 1 diabetes are dependent on giving themselves shots of insulin to survive. In order to determine how much insulin they need, it's important for them to monitor their blood glucose carefully - usually multiple times each day.
While there is no known cure for type 1 diabetes, people with this disease can live very full and healthy lives by carefully controlling their glucose with proper insulin administration and a healthy diet.
Type 2 Diabetes & Insulin Resistance
People with type 2 diabetes produce insulin, it just isn’t doing its job properly. At one time, their insulin worked well - but it got burnt out and lazy. Over time, insulin resistance develops in these individuals. Insulin resistance is the term used to describe the inability of insulin to work properly.
The cells in people with type 2 diabetes start ignoring insulin. Even though there is excess glucose in the bloodstream, insulin isn’t able to ‘open the door’ to allow glucose to enter the cells for use and it also isn’t able to store excess glucose like it should (5) .
The good news is that people with type 2 diabetes can often start making healthy insulin again, if they take care of themselves in the right way.
Type 2 Diabetes Symptoms
The symptoms of type 2 diabetes are similar to those of type 1 diabetes, although they may occur more slowly and not be as noticeable in the early stages of the disease. However, these initial symptoms that may be barely noticeable at first can progress as the disease advances and lead to dangerous complications.
Symptoms of Diabetes Include:
- Polyuria (frequent urination)
- Polydypsia (frequent thirst)
- Vision Problems
- Numbness in Hands and Feet
- Sexual Problems
- Generalized Weakness
- Fatigue
Type 2 diabetics more frequently have additional symptoms resulting from their insulin resistance that type 1 diabetics don’t as commonly experience. These include:
- Rash (Acanthosis Nigricans)
- Hypertension
- Dyslipidemia
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
Type 2 Diabetes Causes
Type 2 diabetes is the result of insulin that doesn’t function well. Sometimes there is also not enough insulin produced in people with type 2 diabetes. The amount of insulin that is produced and functional can vary dramatically between different people with type 2 diabetes.
But what exactly causes the insulin to malfunction? On a cellular level, this isn’t exactly clear.
What is known is that there are well-defined risk factors that significantly contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes.
Type 2 Diabetes Risk Factors
- Overweight & Obesity
- Smoking
- Sedentary Lifestyle
- Family History
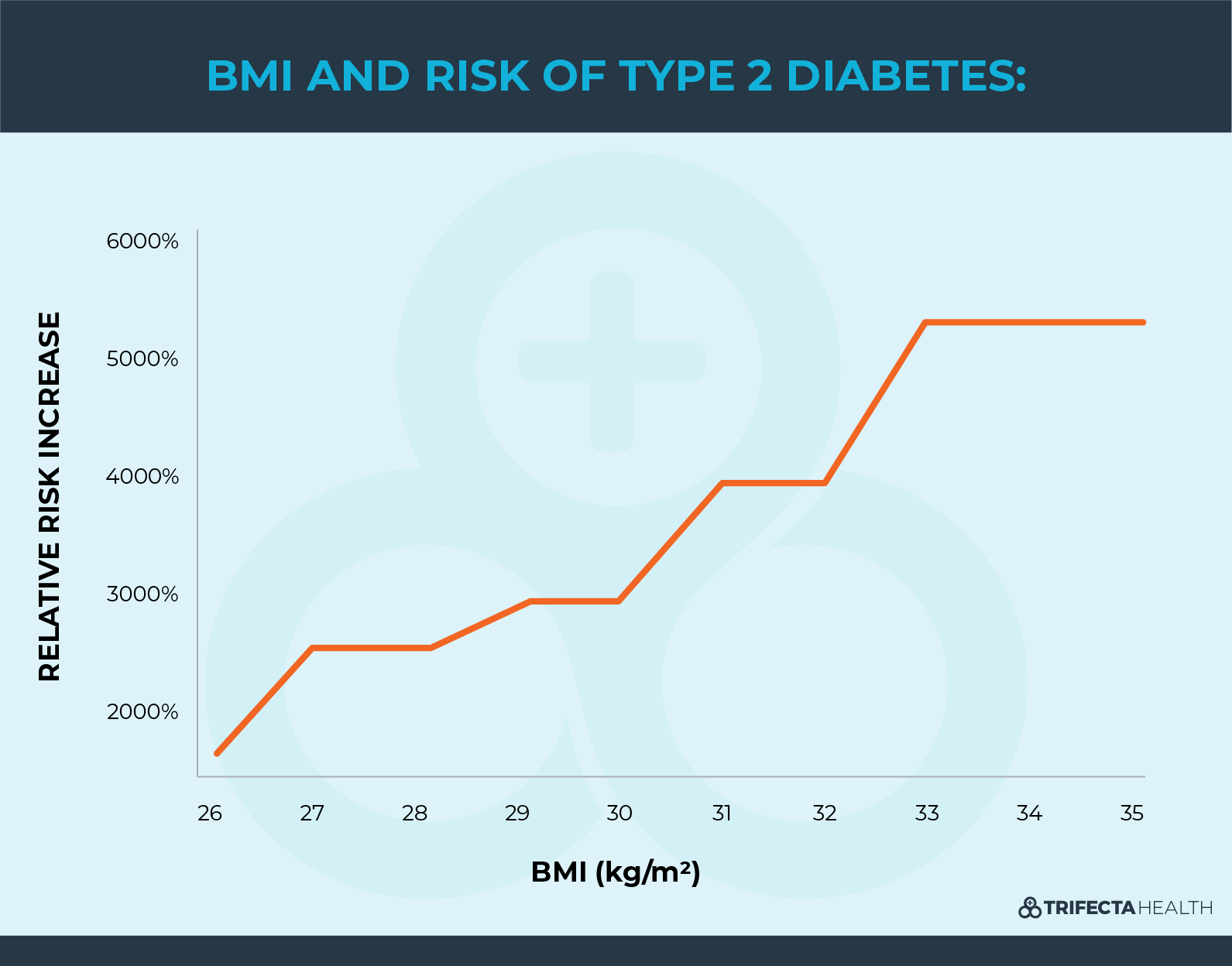
Is Type 2 Diabetes Genetic?
Yes. There seems to be a strong genetic component to developing type 2 diabetes. About 75 to 90% of affected individuals have a close relative with the disease. The familial link is surprisingly much higher for people with type 2 than type 1 diabetes (6).
But don’t think that just because your parents have type 2 diabetes, you will too. Remember, type 2 diabetes is often a preventable disease.
This familial link appears complex and strongly influenced by environmental factors, like diet and exercise. This means that families living together often share a similar lifestyle, including eating the same food types and engaging in relatively similar amounts of physical activities. Because diet and exercise are so important in the development of type 2 diabetes, families with an unhealthy diet and sedentary lifestyle are all more likely to develop type 2 diabetes.
Therefore while your genes may impart some influence on disease development, your lifestyle choices can almost always overcome your genetic susceptibility. Even if your entire family has type 2 diabetes, you can prevent developing the disease by taking diet choices and exercise seriously and successfully maintaining your optimal weight. On the contrary, you will still have a high likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes if you engage in high risk lifestyle behavior, even if no one else in your family has type 2 diabetes.
Type 2 Diabetes Complications
Both emergent complications and long term consequences of diabetes are significant and common. These are some of the problems type 2 diabetics can experience:
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
- Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State (HHS)
- Kidney Disease & Failure
- Heart Disease
- Stroke
- Vascular Disease
- Poor Wound Healing
- Immunosuppression (Frequent Infections)
- Nerve Damage
- Gastroparesis
- Sexual Dysfunction
- Pregnancy Related Problems
- Hypoglycemia (Diabetic Medication Side Effect)
Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosis
Diabetes can be diagnosed with a blood test. The most common test you may hear about is blood glucose, which is a measure of your blood sugar at the current moment you have it checked. A fasting blood glucose is usually used to make the diagnosis of diabetes.
However, blood sugars that are greater than 200 mg/dl taken at anytime are also typically indicative of the disease. Everyone with diabetes should regularly check their blood sugars to ensure they are staying well controlled.
Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) is another blood test that can be used to both diagnose diabetes and track whether an individual's diabetes is getting better or worse over time.
HbA1c is a marker of the average blood sugar over the past few months. A HbA1c greater than 6 is usually diagnostic of diabetes. Type 2 diabetics that are able to get their hemoglobin A1c less than 6 may successfully be in remission from the disease.
If you are diagnosed with diabetes, you should work with a diabetes educator to help get you started on learning how to best manage and treat the disease.
Type 2 Diabetes Treatment
The overarching goal of type 2 diabetes is to achieve normoglycemia (normal blood sugar levels) as well as to minimize other risk factors contributing to the disease and other comorbid disease processes.
Comorbid diseases are a group of diseases that tend to occur together in the same person at the same time. This is frequently because they have the same risk factors.
For example in this discussion, being overweight with an unhealthy diet and low levels of physical activity are risk factors for the comorbid conditions diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol, congestive heart failure, stroke, and more.
The holistic treatment for type 2 diabetes involves a combination of lifestyle changes.
1) Type 2 Diabetes Diet
Improving nutritional intake is paramount in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. While this can be complicated and varies based on the individual's needs and lifestyle, basic principles are rooted in managing carbohydrates (glycemic load), improving insulin sensitivity, reducing the risk factors of comorbid conditions and weight loss through calorie control.

LEAN PROTEIN
Lean protein, either meat or plant based offers an onslaught of health benefits. Among a variety of other functions, it provides you with the building blocks your body needs to repair tissue, build and maintain muscle and bones, and make important hormones and enzymes. Protein has also been shown to help with weight loss by making you feel more full (and therefore consume fewer calories).
UNSATURATED FATS
Not all fats are created equal. And some of them are good for you. Healthy fats (aka monosaturated fats) can increase the 'good cholesterol' (HDL) and lower 'bad cholesterol' (LDL). If they are used to replace carbohydrates or unhealthy fats, they can also help lower blood pressure. However all fats, even healthy ones, contain higher calories than the other macronutrients. Therefore it is important to be mindful of portion sizes and count calories when you're including them in your diet.
VEGETABLES
Vegetables (especially leafy green vegetables) are not surprisingly, really healthy. They are ideally low in calories and rich in a variety of nutrients including vitamins, minerals and antioxidants that supports our bodily functions. They are high in fiber and are a low digestible carbohydrate, making them a 'good carbohydrate' choice. They provide the volume so many of us crave, allowing us to eat large quantities of food for very low calories and high nutritional value.
FRUIT
While diabetics (especially type 1 diabetics) do need to be careful about the quantity and type of fruit they eat due to the sugar it contains, fresh fruit can offer many health benefits. They are high in fiber and many nutrients including vitamins and antioxidants. They also can satisfy the 'sweet tooth' in many of us with a low calorie and nutritious delivery.
WHOLE GRAINS
There is a tremendous amount of evidence to support how good whole grains are for us. They provide an excellent source of fiber and a slew of other nutrients. They have been shown to significantly improve our heart health and decrease the risk of many chronic health conditions including diabetes, heart disease, and some cancers. In fact they have been shown to improve overall mortality. While whole grains are good carbohydrates and a very important part of a healthy diet, they do still need to be counted in the diabetics daily carbohydrate intake.
FIBER
Among many other health benefits, high fiber may improve glycemic control. It’s recommended to include at least 14 grams for every 1000 calories of food you consume.
Diabetic Diets Should Avoid:
- Added Sugar
- Saturated Fats
- Processed Foods
- Salt
Added Sugar
If you are diabetic, or just trying to eat a healthier diet, avoiding all foods with added sugar is an ideal place to start. Added sugar provides no additional nutritional value, and is directly linked to the cause and progression of diabetes. It leads to fast spikes in blood glucose and weight gain. This is different than natural sugars found in fruits and some vegetables as these sugars are more slowly absorbed in the body and mixed with fiber and other vital nutrients.
Saturated Fats
Saturated fats contribute to ‘bad cholesterol’ (LDL) and therefore contribute to increasing the risk of high cholesterol (hypercholesterolemia) and high triglycerides (hypertriglyceridemia). They also contribute to damaging the vessels in your body (atherosclerosis) and increase the risk of heart disease and other vascular diseases including stroke. They are also high in calories leading to weight gain without much nutritional value.
Processed Foods
Processed foods tend to be high in calories with high glycemic index, and without many nutrients.
Salt
Low Salt (<2300mg/day) is encouraged as it helps decrease other risk factors including high blood pressure and heart disease. Your doctor may recommend this number to be even lower if you already have high blood pressure or heart disease.
2) Weight Loss
Obesity is one of the largest risk factors for type 2 diabetes and weight loss with healthy weight maintenance can in of itself treat the disease. It also reduces the risk and helps with the treatment of other comorbid conditions like hypertension and hyperlipidemia. While diet and exercise are the ideal combinations in achieving weight loss goals, other options such as bariatric surgery may be considered in some people.

3) Exercise
Exercise not only contributes to weight loss, it independently can improve glucose control in people with diabetes. Increased physical activity also decreases the risk for and improves the disease process of comorbid conditions such as cardiovascular disease and hypertension.
It can also have a powerfully positive effect on our psyche and can improve symptoms of many mental health conditions including anxiety and depression. This has shown to lead to improved lifestyle choices including healthier food choices, weight loss, and decreased use of unhealthy substances like smoking and alcohol.
4) Smoking Cessation
Quitting smoking not only can improve glycemic control, it also significantly reduces the risk of other comorbid conditions such as cardiovascular disease and hypertension. Not to mention that abstaining from smoking reduces so many other serious medical conditions including many cancers and lung disease. Smoking is bad for your body in so many ways. Just quit smoking.
5) Type 2 Diabetes Medications
Many people with type 2 diabetes may not need medications at first. If caught early enough,changing your lifestyle by modifying your diet and increasing exercise can be enough to control and eliminate the disease altogether.
While many people may feel it is not ideal, starting medications for type 2 diabetes is common. As described above, this disease can become very dangerous if it is not well controlled. It is therefore very important to regularly take all medications your doctor prescribes. Your doctor may recommend oral medications in addition to the recommended lifestyle changes. In advanced cases of type 2 diabetes, insulin injections may be required as well.
Is Type 2 Diabetes Curable?
The amazing news about type 2 diabetes is that many cases can be cured.
Reversing Type 2 Diabetes
Reversing type 2 diabetes is extremely difficult, but is possible to achieve in most people suffering from the disease. Successfully getting rid of diabetes is enormously dependent on learning the right lifestyle modifications and following them consistently. The goal is to get your HbA1c < 6 and your blood glucose in normal ranges.
If you’re taking medications for type 2 diabetes, try looking at them like a temporary assistant that can help you get back on track while diet and exercise do their job.
It’s important to work with your doctor and a nutritionist to develop the right diet and exercise regimen for you. Actually following these regimens by consistently eating well and regularly exercising is always the hardest part. But reaping the rewards of a lifetime of a healthier and happier life are well worth the initial struggle.
Make sticking to a healthy diabetic diet easier than ever with diabetic meal delivery. Get nutritious, balanced meals cooked and shipped right to your door!