It’s hard to overemphasize the impact obesity can have on our health. It continues to be the leading cause of preventable death in the United States. Declared a true epidemic, the prevalence of obesity in the United States reached a whopping 40% (39.8%) in 2015-2016 .
People that are obese consistently have an increased mortality, which means that studies show they don’t live as long as people who aren’t obese (1). Obese individuals also have significantly increased morbidity, which means that studies show they suffer significantly more health problems than people who are not obese.
This article is all about obesity, it's life altering influences, why our country is so affected by this preventable condition and how can we take the steps we need to change.
Obesity Definition
Let’s start by looking at how obesity is defined.
Body Mass Index (BMI)
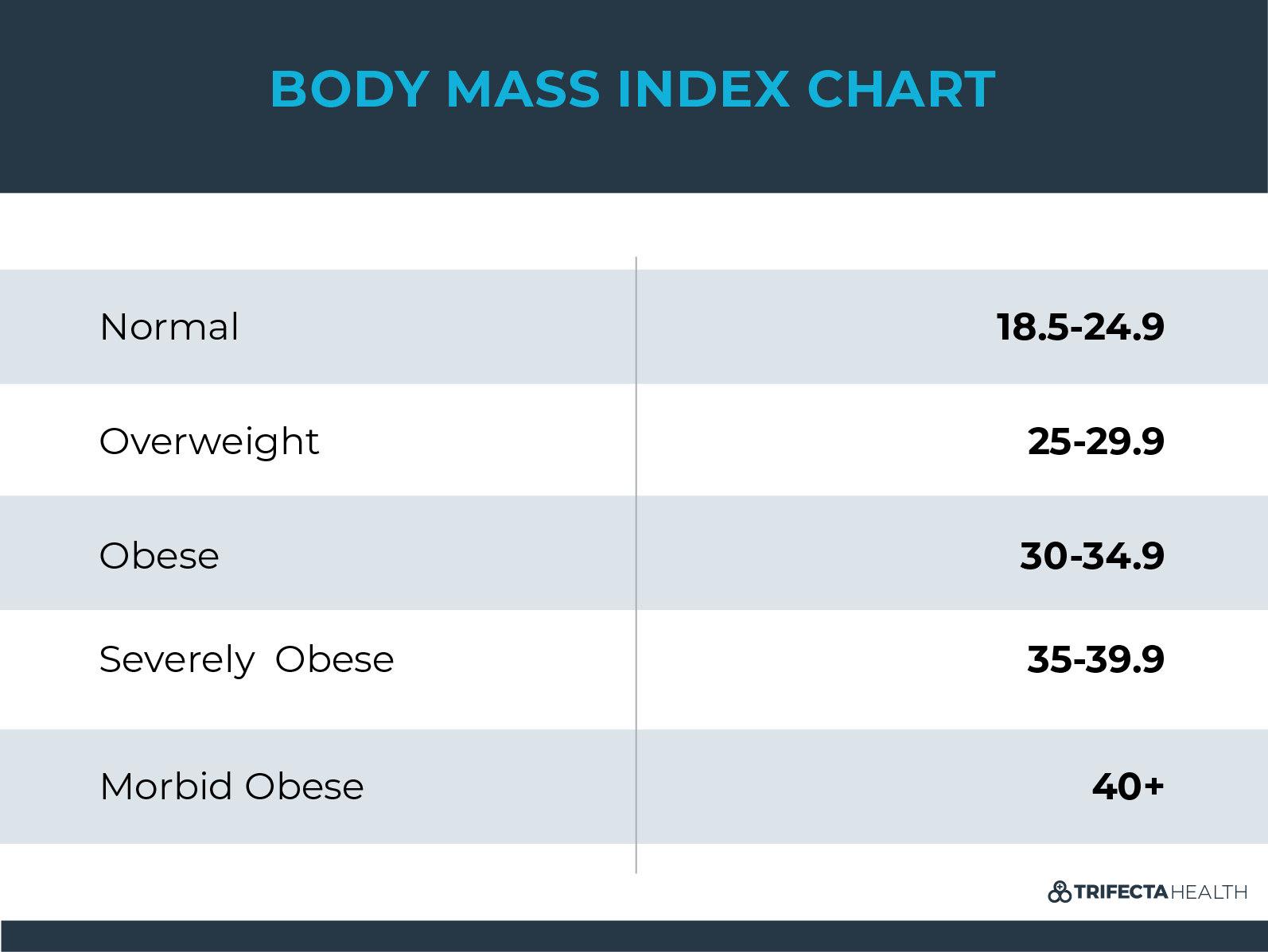
The most common way to estimate extra fat is by calculating a BMI (body mass index). BMI can quickly create this estimate by comparing the weight of a person to their height.
A BMI of 30 or more defines obesity.
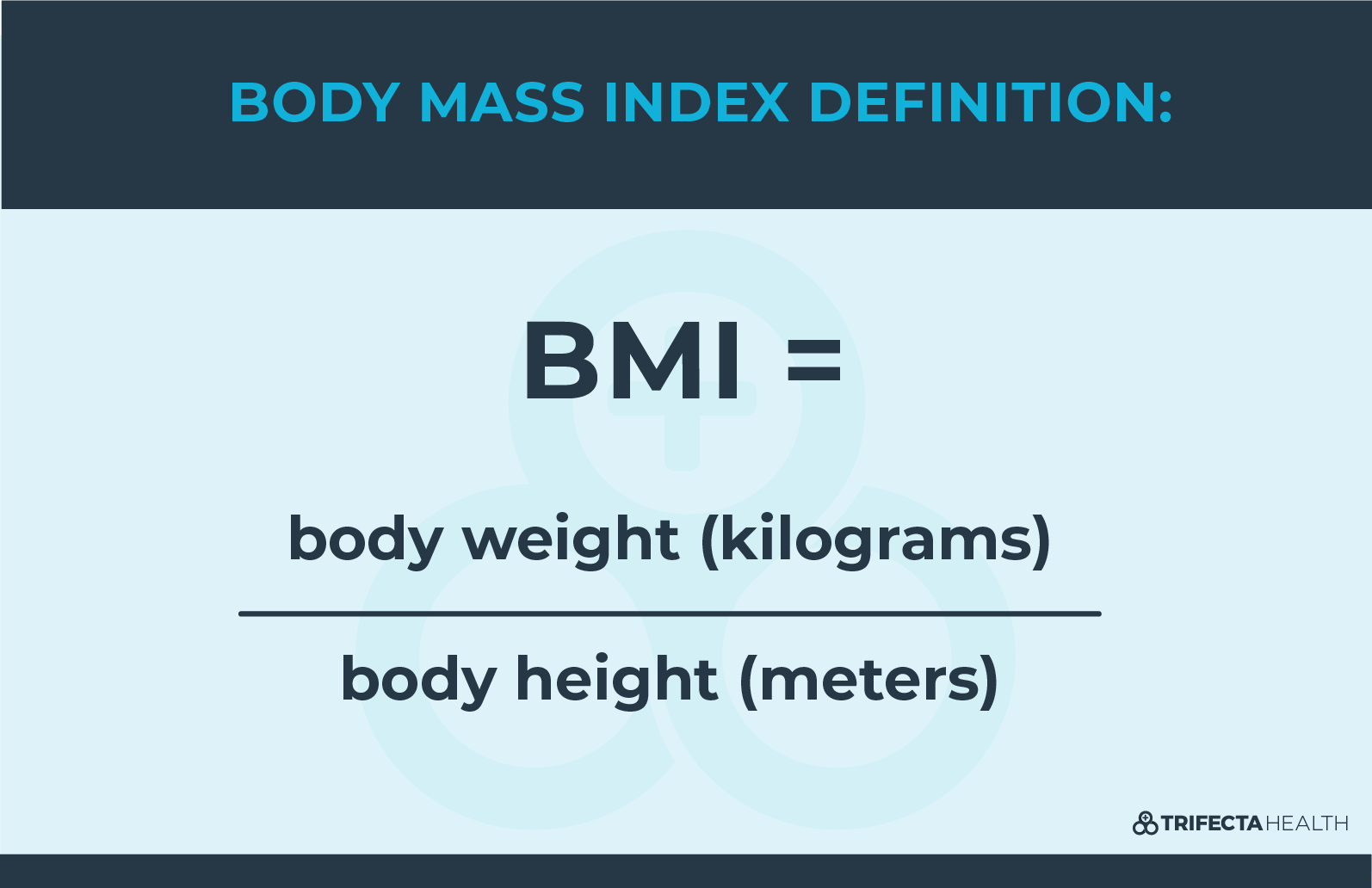
Because everyone has different amounts of muscle, and muscle weighs more than body fat, BMI can be an inaccurate estimation of fat in very muscular individuals. For example, a body builder will likely have a high BMI but an exceptionally low percentage of fat, and is obviously not considered obese.
Morbid Obesity
Morbid obesity is often mistakenly thought to represent people who are severely obesity. But this isn’t exactly true. Instead, morbid obesity refers to anyone who is obese with health complications caused by their obesity.
Childhood Obesity
Part of what seems so unfair is that the lifestyle patterns leading to such significant weight gain frequently begin in childhood or even infancy. And the cause and significant influence that this weight gain has on health is not understood by many overweight adults. In an ever-cyclical manner, these affected adults naturally raise their children with similar eating and lifestyle habits - leading to more obesity.
Education and perspective are key.
It can be significantly harder for people who were obese as children to achieve a healthy weight.
Obesity Health Risks
The health consequences of obesity are vast. Because obesity is such a major risk factor for a variety of medical problems, people who are obese tend to have many of these problems at the same time – and are at a higher risk for the others. These diseases are referred to as ‘comorbid’ conditions.
The good news about each of these conditions is that weight loss also often improves these conditions and reduces the risk of developing other comorbid diseases.
- Hypertension
- Type 2 Diabetes
- High Cholesterol
- Bone Problems
- Sleep Apnea
- Cancer
- Heart Problems
- Stroke
- Kidney Disease
- Gout
- Gastric Reflux
- Dementia
- Liver & Gallbladder Problems
- Blood Clots
- Infections
- Skin Problems
- Pregnancy Problems
- Emotional & Psychosocial Consequences of Obesity
Obesity Treatment
In addition to the devastating effects it imposes on the affected individual, obesity has tremendous economic influence on the country as a whole – costing $147 billion dollars in 2008 alone (1).
Treating obesity must start with education. In a society filled with calorie packed processed food and every convenient transportation to support a sedentary and stressed lifestyle, spreading awareness of how to avoid these pitfalls is key to treatment as well as disease control and prevention.
Obesity Diet
It seems like there is always a new fad weight loss diet promising premium results. So which diet really is best for weight loss?
The calorie controlled diet that you will be the most consistent with is the diet that will work for you.
An overwhelming amount of research supports that calorie control in any diet (ie: eating fewer calories than you burn) will result in effective weight loss. Learning to not eat more calories than you burn is paramount in the overweight and obesity battle.
Some research supports that low carbohydrate diets may add extra benefit for weight loss in obesity. Eating heart healthy whole grains, fresh fruits and vegetables and minimizing processed food leads to additional health boosts.
Bottom line: the most successful diet will be the calorie-controlled diet that you can stick to.
Exercise
The mainstay of dieting is “calories in, calories out”. The ‘calories out’ portion is exercise.
Regular physical activity including cardiovascular exercise daily for at least 30 minutes is a great place to start. Consistency is key. Don’t get discouraged if you’re not running a marathon right away. Any activity that gets your heart rate up for an extended period of time - including walking, running, swimming, biking - is effective cardiovascular exercise.
With this daily practice, you’ll gradually be able to increase both the duration and frequency of your activity. Tailor the exercise to fit you.
Emotional Well Being
Anxiety and depression are so common throughout our society. These conditions are also strongly linked to unhealthy eating habits and therefore obesity along with all of the health problems that go with it.
It’s so easy to put taking care of ourselves aside. But investing in your emotional well-being will reap a ripple of rewards. Meditating, engaging in talk therapy, exercising, eating well, and other lifestyle modifications to foster effective stress management are critical and all too frequently undervalued pillars supporting our long term health.
Weight Loss Medications
Unfortunately, there’s no magic pill to make you lose weight. Most of the weight loss medications advertised are not shown to help weight loss in any way and many can be dangerous.
There are a few prescription medications that can contribute to helping with weight loss in some people by helping to decrease anxiety, depression or appetite. These are in no way a quick fix – diet and exercise are always key.
Because so many of the medications or supplements advertised for weight loss can cause such bad side effects (and because so many of them don’t work) it’s critically important to always talk to your doctor before taking any medications to lose weight.
Weight Loss Surgery
Bariatric surgery is becoming an increasingly popular weight loss strategy. This is major surgery - and shouldn’t be taken lightly. It works by making the stomach smaller.
With a smaller stomach people theoretically become fuller faster. But this will only lead to weight loss if they actually stop eating when they’re full.
While bariatric surgery is very successful for some, many others push past the full feeling and continue to consume many more calories than they burn. Unfortunately this leads to many people either not experiencing successful weight loss, or quickly regaining weight they initially lost after surgery.
Bottom line: There is such a strong psychological component to overeating that it is essential to holistically address the emotional and lifestyle components of obesity. Consistent healthy eating and active lifestyle are key to successful weight management.