Here are the risks of following a Starvation Diet:
- Developed eating disorders
- Decreased metabolism
- Weakened immune system
- Poor body temperature control
- Weakness and fatigue
- Impaired cognitive function
- Heart problems
- Organ damage
If you are trying to lose weight, it is well understood that cutting calories below your daily energy needs is the most efficient pathway to drop pounds. But how low can you cut your calories before your body begins to see negative effects?
Starving yourself may seem like an easy way to eliminate calories and lose weight, but this likely only works for a short time period and sticking to a starvation diet plan for more than a few days may do more harm than good.
What is a Starvation Diet?
A starvation diet is any diet that consistently restricts calories below your baseline needs for survival and normal bodily functions, with the intention to lose weight quickly. Starvation diets are also commonly referred to as “crash diets”.
One can easily argue that intermittent fasting, extended fasts, or even very low calorie diets monitored by a physician fall into this category. However, it is the intention, length of the period of starvation, and average calorie consumption that can help to distinguish a starvation diet from another weight loss diet plan.
How Long Do Starvation Diets Last?
Starvation diets intend to restrict calories below baseline needs for extended periods of time in the hopes of losing body fat. This typically is achieved over multiple weeks, or in the case of a developed eating disorder, months or years.
How Many Calories Does Your Body Need to Survive?
Your baseline calorie needs are often referred to as your BMR or basal metabolic rate (also called your resting energy expenditure, REE). This is how many calories your body needs to maintain your organs in a state of rest (1).
Knowing your BMR is a good starting place in determining what calorie level you should strive for in your average calorie consumption. Using average calories is more efficient than only tracking daily intake, as this allows you to include fasting windows and calculate your consistent intake over multiple weeks.
Calculate your BMI here:
Your average calorie consumption is the amount of calories you consume on average over a given period of time
Your BMR depends on your height, weight, age, body composition, and overall health, and does not account for any movement or daily activity.
For the average individual, it takes roughly 1,320 calories to support your liver, brain, heart, and kidneys each day - this amount falls below many of the popular weight loss diet plans that recommend 1,200 calorie diets (2,3).
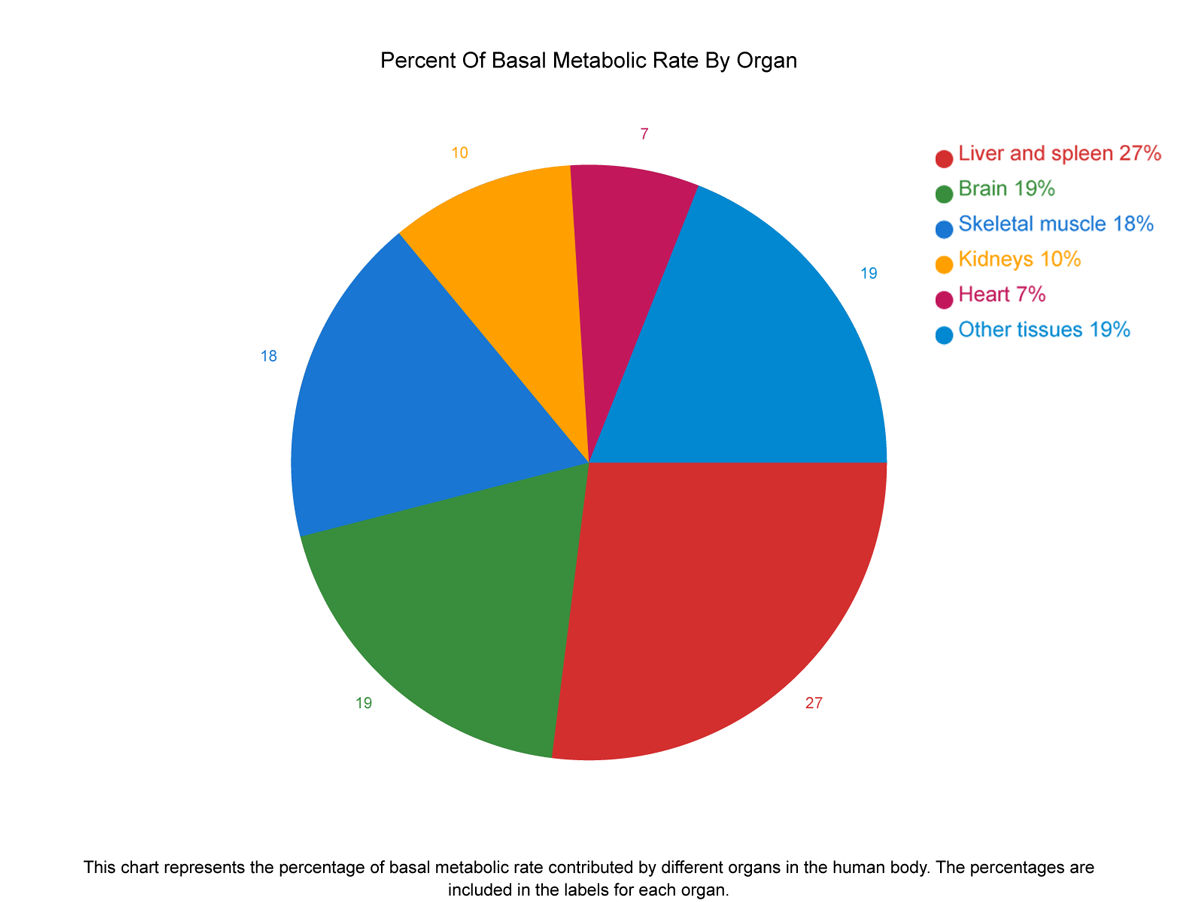
Majority of these calorie needs come from your heart and kidneys, requiring about 440 calories per day each. And your brain accounts for almost 20% of your daily energy requirements, utilizing anywhere from 300 to 500 calories a day just to think.

It is possible to follow a very low diet below your BMR needs, but it is not recommended long term or without the support of a physician regularly monitoring your health and nutrition status.
What Happens to the Body When You Starve (Starvation Mode)?
If you are cutting calories, you will lose weight. However this does not mean that a being in a state of starvation will help you safely lose a lot of weight or keep it off long term. In addition, losing weight quickly does not mean you will lose more weight overall - many times, the slow sustainable approach is much more effective in the end (4,5,6).
After a few days of fasting or severe calorie restriction, your body will begin to lose weight from breaking down bodily stores for energy. However, the success seen with this approach is fairly short lived and not sustainable.
Your body is primed for survival over just about everything else and when you stop feeding it, eventually it switches gears to help compensate for the loss of food. This includes slowing your metabolism to decrease energy needs, slowing down various bodily functions, and shifting appetite regulating hormones (7,8,9,10). This state is commonly referred to as starvation mode.
If you continue to starve yourself, you may start to experience the effects of malnutrition or put your health in serious risk. You might also find that it is very difficult to maintain your weight loss once you resume eating due to the impacts on your metabolism, appetite, etc. This results in some of the overeating and weight gain commonly seen with yo yo dieting.
There is nothing more discouraging than not being able to stick to your diet and then gaining weight as a result of being overly restrictive.
What Are the Risks of Following a Starvation Diet?
The truth is, we can survive for quite some time without food and regular fasting windows are likely not detrimental to our long term health - as long as you resume a balanced diet in between.
However, following a starvation diet long term can have serious health implications, including:
- Developed Eating Disorder
- Decreased Metabolism
- Weakened Immune System
- Poor Body Temperature Control
- Weakness and Fatigue
- Impaired Cognitive Function
- Heart Problems
- Organ Damage
Developed Eating Disorders
Utilizing starvation as a tool for weight loss is a form of disordered eating that can lead to a diagnosed eating disorder.
Decreased Metabolism
Starvation diets slow your metabolism and eat away at your precious muscle mass, both of which will cause you to burn fewer calories.
Weakened Immune System
Hunger puts stress on the body’s cells and starvation is associated with decreased expression of genes associated with immunity. Additionally, malnutrition can negatively impact your immune function.
Poor Body Temperature Control
Starvation also lowers body temperature causing you to feel cold and have trouble maintaining a comfortable body temp.
Weakness and Fatigue
Lack of calories, low blood pressure, and low blood glucose associated with starvation diets can make you feel depleted, tired, and weak.
Impaired Cognitive Function
When your brain goes into survival mode, it can lead to depression, anxiety, irritability, poor mood regulation, impaired concentration, decreased alertness, and poor problem solving.
Heart Problems
A slowed heartbeat is one of the compensations your body makes during starvation. Over time this can lead to decreased size of the heart and serious heart problems.
Organ Damage
Without enough calories and nutrition, many of your body’s organs will become impaired and some can start shutting down over time. This damage can be permanent and lead to death.
How to Eat Fewer Calories Without Starving Yourself
Sure starving your body works as a temporary approach to fast weight loss, but the price of starvation is likely not worth the risks. Instead of making food the enemy, aim to develop a healthy balanced approach to nutrition that allows you to nourish your body while still supporting your weight loss goals. This will ensure you develop healthy habits that last and that keep the weight off for good.
Consistency is everything when it comes to results. Stay consistent and start losing weight quickly with ready-made low calorie meals cooked and shipped to your door.

